In short: The Dow Jones measures the 30 largest companies in the U.S.A.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is perhaps the most widely followed stock market index in the world. Yet, very few people actually know what that the number represents just 30 companies. The following history and explanation of the DJIA will help you become one of the few people who actually know what it means when you hear the Dow discussed in the nightly news.
The Birth of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
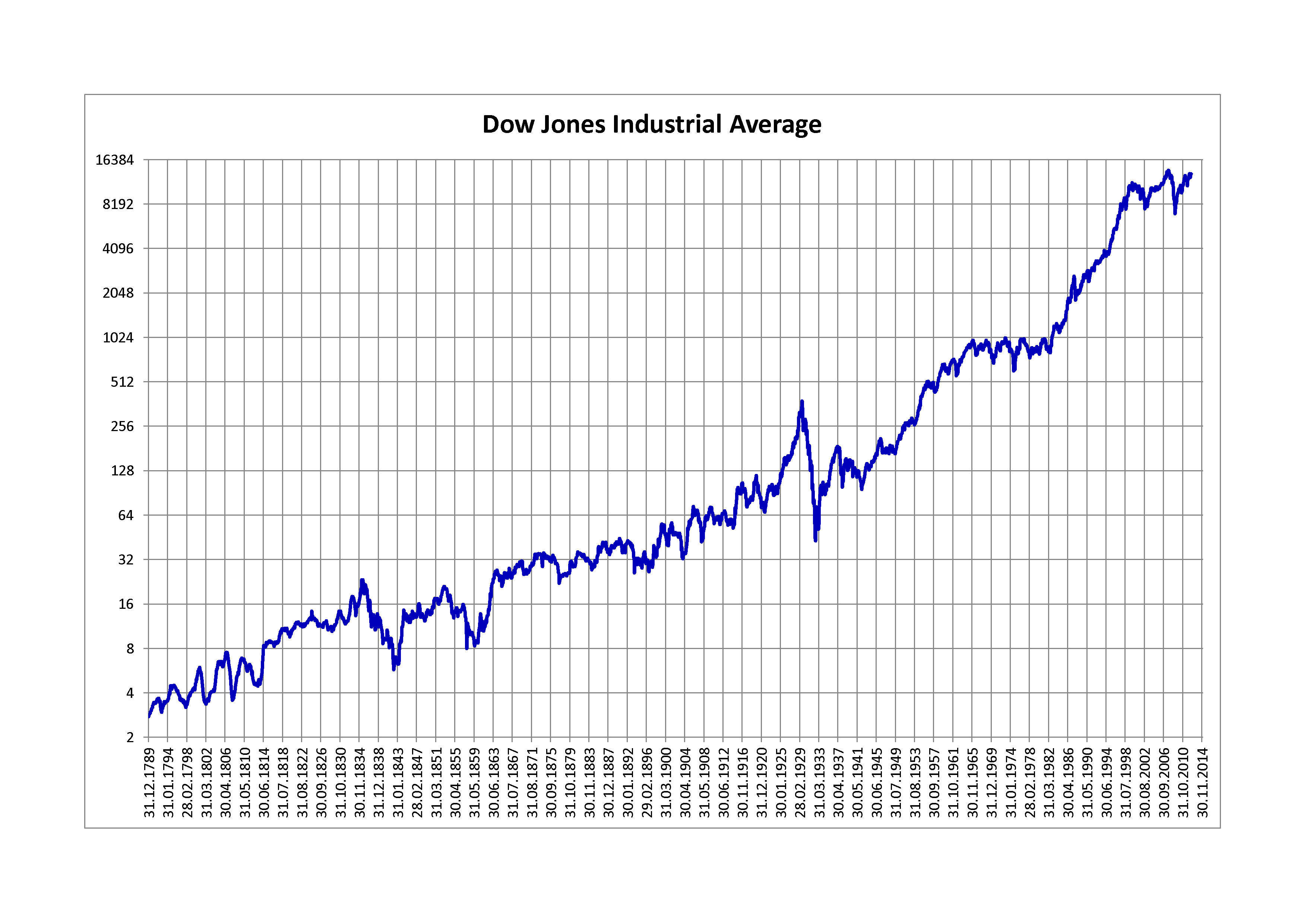
The Dow Jones Industrial Average was introduced on May 26, 1896. The Dow was created by a man named Charles H. Dow, one of the founders of Dow Jones & Company, which was formed in 1882.
Dow’s first index was created in 1884, and consisted of 11 transportation-related stocks. He adjusted the original index (on Wall Street, this process is known as “reconstituting”) and renamed it the Dow Jones Rail Average (in the 1970’s, the name was updated to the Dow Jones Transportation Average to cover the introduction of air freight and other forms of transportation).
Dow soon realized that industrial companies were quickly becoming more important than railroads. He then created a new index of stocks consisting of twelve companies and called it the Dow Jones Industrial Average or DJIA for short. The index originally consisted of industrial-sector companies, including those focused on cotton, sugar, tobacco, and gas.
To calculate the reported index figures, Dow added up the stock price of selected companies, divided by the number of companies in the index at the time.
The very first published Dow Jones Industrial Average figure was 40.94. In simple terms, it means that the average stock price of the twelve stocks Mr. Dow had chosen was $40.94.
The Original 12 Dow Jones Stocks
The original twelve stocks in the Dow Jones Industrial Average consisted almost entirely of commodity-based firms and were as follows:
- American Cotton Oil Company
- American Sugar Company
- American Tobacco Company
- Chicago Gas Company
- Distilling & Cattle Feeding Company
- General Electric
- Laclede Gas Company
- National Lead Company
- North American Utility Company
- Tennessee Coal & Iron
- U.S. Leather Company (Preferred)
- U.S. Rubber Company
At the time, these were large, profitable, and highly respected firms. Most were eventually replaced in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
